For this task I glossed over the key terms for this room, and agreed to not complain too much which might be a struggle but I powered through.
Also, to answer the question SSH keys are protected with a passphrase.
Encryption is used to keep all our information private and inaccessible (for the most part) from threat actors! Now after reading their material we can answer their questions.
What does SSH stand for? Secure Shell
[This answer can be looked up if not already known.]
How do web servers prove their identity? Certificates
What is the main set of standards you need to comply with if you store or process payment card details? PCI-DSS
Task Completed!
Math is the foundation of cryptography and so in this task we do exactly that. Math.
What’s 30 % 5? 0
[30 is divisible by 5 with no remainder.]
What’s 25 % 7? 4
[Seven times three equals 21 with a remainder of 4 to get to 25.]
What’s 118613842 % 9091? 3565
[118613842 divided by 9091 is ~13047.39 so it’s apparent that it will have a remainder. If you just multiply 9091 by 13047 and subtract the total from 118613842 you’ll get 3565 as the remainder.]
Task Completed!
The main types of encryption are symmetric and asymmetric where each has their strength and weakness. Symmetric encryption uses the same encrypt and decrypt key while asymmetric uses a different key for each.
Should you trust DES? [Yea/Nay] Nay
DES is only 56 bits long, which is too short to be considered secure.
What was the result of the attempt to make DES more secure so that it could be used for longer? Triple DES
Since DES was able to be brute-forced to provide the keys, it was proposed to tweak the encryption algorithm with three 56-bit keys making it not as susceptible to brute-force attacks. Here’s an article describing Triple DES.
Is it ok to share your public key? [Yea/Nay] Yea
When encrypting information asymmetrically you have to be able to decrypt the data so sharing your public key enables others to view the information you’ve sent/shared. You do not want to share your private key as someone can impersonate you.
Task Completed!
RSA is an algorithm that generates public/private keys and is commonly used in CTF challenges. After reading this section there is a question:
p = 4391, q = 6659. What is n? 29239669
The variable n is calculated by getting the product of p and q which are given.
After learning about RSA and the variables we can continue. Task Completed!
Asymmetric encryption can be used for establishing symmetric encryption for faster communication. That was it for this task.
While users can encrypt/decrypt information between users with public/private keys, websites use certificates to verify their identity.
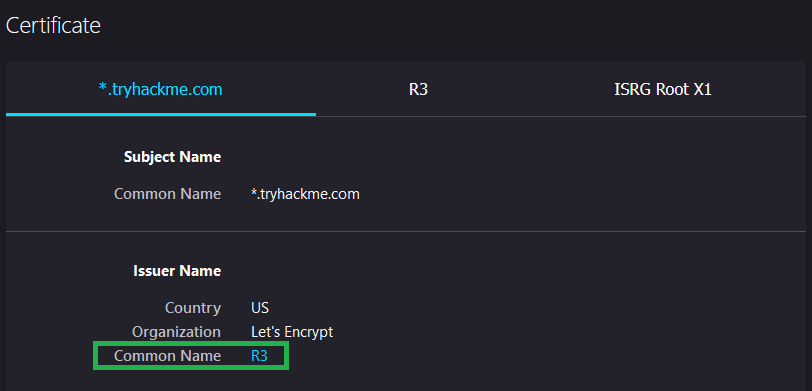
Who is TryHackMe’s HTTPS certificate issued by? R3
THM’s certificate can be accessed by clicking on the lock symbol by the URL and selecting ‘More Information’. Another window titled ‘Page Info’ should provide an option to ‘View Certificate’. Once selected you can view who issued the certificate:
Task Completed!
SSH is used to securely connect to a computer with an authentication key and is the focus of this task. To give this topic hands-on usage I started up a VM and downloaded the SSH Private Key provided.
I then opened the file in notepad.
What algorithm does the key use? RSA
[This can also be seen in the file name which was idrsa.id_rsa]
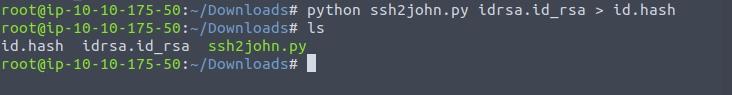
In order to crack the passphrase for the provided key, I copied the RSA file to the kali VM and used John The Ripper’s SSH algorithm to provide a hash of the private key:
Then I ran it against the rockyou wordlist provided in the VM using John The Ripper:
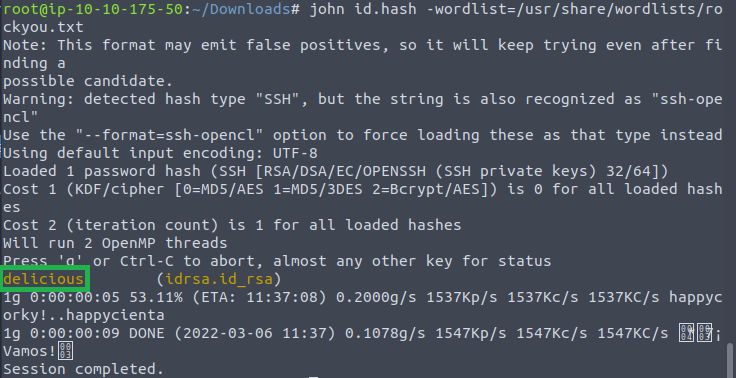
Crack the password with John The Ripper and rockyou, what’s the passphrase for the key? Delicious
Task Completed!
This task just briefly discusses the mentioned key exchange as an alternate of the process discussed in Task 7.
This task discusses PGP, it’s open source alternative GPG, and AES, the more secure version of DES with longer keys.
This task also provided a gpg zip file for us to decrypt the message. I first downloaded the file to the kali VM on THM and imported the provided key:
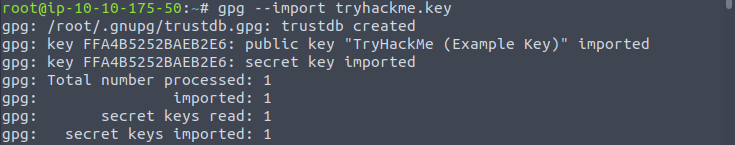
Then by decrypting the message and viewing the file:
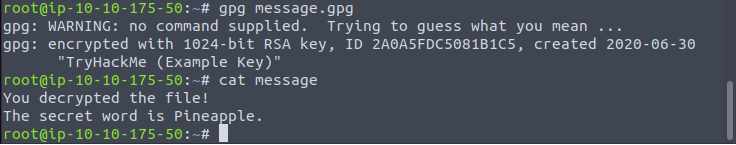
What’s the secret word? Pineapple
Task Completed!
After reading how quantum computers are the apocalypse for cryptography as some of these methods we’ve learned about will be obsolete, we’ve completed the room!